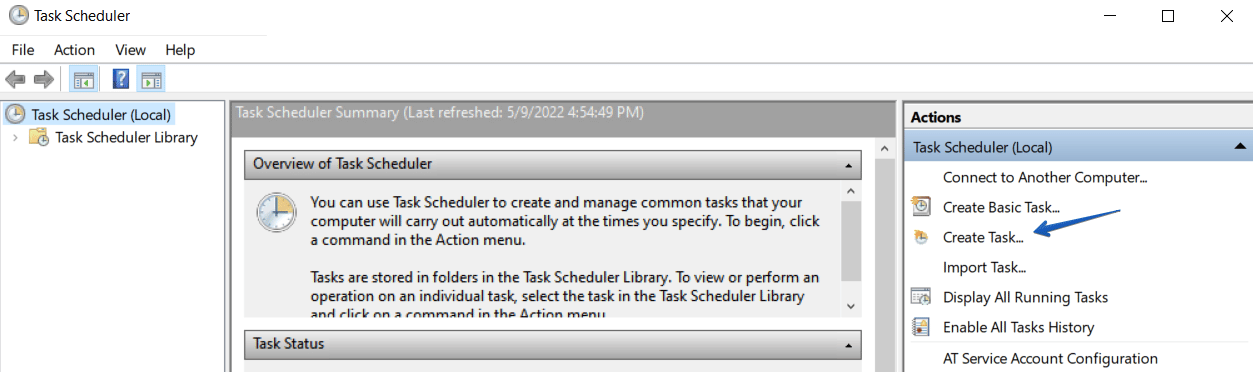
A script can be run via the built-in Windows Task Scheduler tool. It can be found in the “Administrative Tools” section, or by clicking Win+R and typing taskschd.msc. Open the scheduler and in the “Actions” section select Create Task…
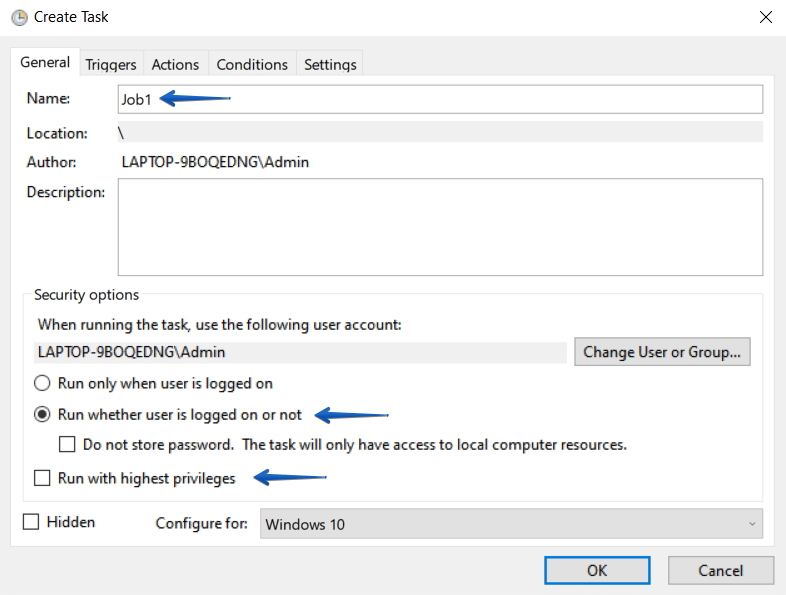
On the “General” tab, specify the name and description of the task, as well as the user on behalf of which the task will be launched (if necessary). In order for the task to be executed regardless of whether the user is logged into the system, select the option “Run whether user is logged on or not.” If the task requires privilege escalation, then check the “Run with highest privileges” option.
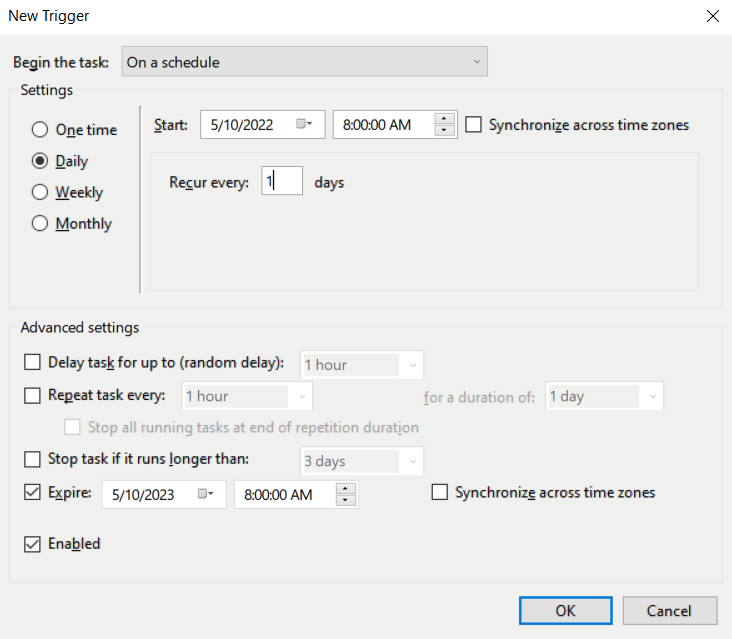
Now, go to the “Triggers” tab and create a new trigger that will store the schedule for launching your task. In the “Start” box, specify the date and time of the start, and in the “Expire” box, the date and time the task is completed. For example, let’s set it to execute the task daily (Daily) and set the repetition period (Recur every) 1 day.
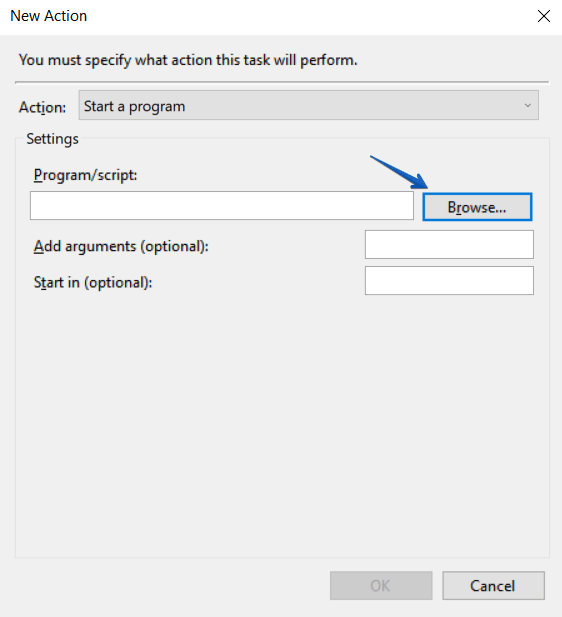
Once the schedule is set, go to the “Actions” tab and add the script you have into the “Program/script” box.
That’s it! Save the task and your script will be performed according to the schedule you set.